Researchers used quantum simulations to acquire new insights into the character of neutrinos—the mysterious subatomic particles that abound all through the universe—and their position within the deaths of large stars.
The examine relied on help from the Quantum Computing Person Program, or QCUP, and the Quantum Science Middle, a nationwide Quantum Data Science Analysis Middle, on the Division of Power’s Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory. The work is printed within the journal Bodily Overview Letters.
“This understanding was one thing new that hasn’t come out of classical computing programs,” stated Martin Savage, the examine’s senior creator and a professor of physics on the College of Washington.
“We acknowledged for the primary time we may examine how entanglement between a number of neutrinos is induced over time, and these outcomes are throughout the error bars of what we might anticipate from a classical pc. It is a step within the course of higher, extra correct and extra scalable quantum simulations.”
Neutrinos end result from nuclear reactions—from the massive reactions that trigger the solar to shine, to the tiny reactions that allow radioactive tracers for medical exams. These extraordinarily gentle particles seem all over the place, carry no electrical cost and infrequently work together with different matter.
However through the collapse and explosion of a star—a course of higher often called a supernova—neutrinos trade power and momentum with not simply one another however with the whole lot round them.
“At this level, the neutrinos go from passive particles—virtually bystanders—to main components that assist drive the collapse,” Savage stated. “Supernovae are attention-grabbing for quite a lot of causes, together with as websites that produce heavy components reminiscent of gold and iron. If we are able to higher perceive neutrinos and their position within the star’s collapse, then we are able to higher decide and predict the speed of occasions reminiscent of a supernova.”
Scientists seldom observe a supernova close-up, however researchers have used classical supercomputers reminiscent of ORNL’s Summit to mannequin points of the method. These instruments alone would not be sufficient to seize the quantum nature of neutrinos.
“These neutrinos are entangled, which implies they’re interacting not simply with their environment and never simply with different neutrinos however with themselves,” Savage stated.
“It is extraordinarily troublesome to simulate this type of system, as a result of entanglement’s an intrinsically quantum-mechanical property past what we are able to seize and approximate in classical computing. That is why we’d like a quantum pc that makes use of calculations based mostly on quantum physics to mannequin what’s occurring.”
Savage and his co-author Marc Illa of the College of Washington’s InQubator for Quantum Simulation obtained an allocation of time on Quantinuum’s H1-1 quantum pc by way of QCUP, a part of the Oak Ridge Management Computing Facility, which awards time on privately owned quantum processors across the nation to help analysis initiatives. The Quantinuum pc makes use of trapped ions as qubits, considered one of a number of quantum computing approaches.
Classical computer systems retailer info in bits equal to both 0 or 1. In different phrases, a classical bit, like a lightweight swap, exists in considered one of two states: on or off.
Quantum computer systems retailer info in qubits, the quantum equal of bits. Qubits, not like classical bits, can exist in multiple state concurrently by way of quantum superposition—extra like a dial with a wider vary of extra detailed settings than an on/off swap. That distinction allows qubits to hold extra info than classical bits. Scientists hope to make use of this elevated capability to gasoline a quantum computing revolution constructed on a brand new technology of units.
That capability allowed Savage and the analysis workforce to simulate an approximation of the quantum-mechanical interactions between a supernova’s neutrinos. An precise supernova would contain a minimal of a septendecillion, or 1054, neutrinos. Savage and Illa started their simulation utilizing an easier mannequin with a system of 12 neutrinos.
Every neutrino “taste,” or kind, present in nature corresponds to a “companion” particle: an electron, muon or tau. The mannequin used within the examine targeted on simply two flavors.
Quantum circuits—the quantum equal of conventional digital circuits—allowed the workforce to mannequin the sophisticated connections and interactions between the particles so that every neutrino may work together with every of the others, not simply its nearest neighbors.
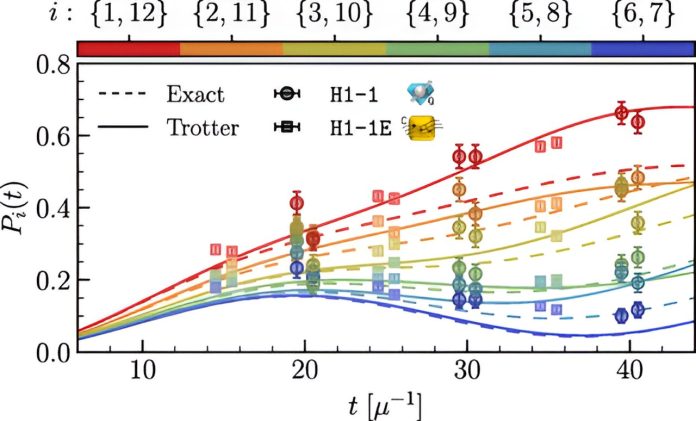
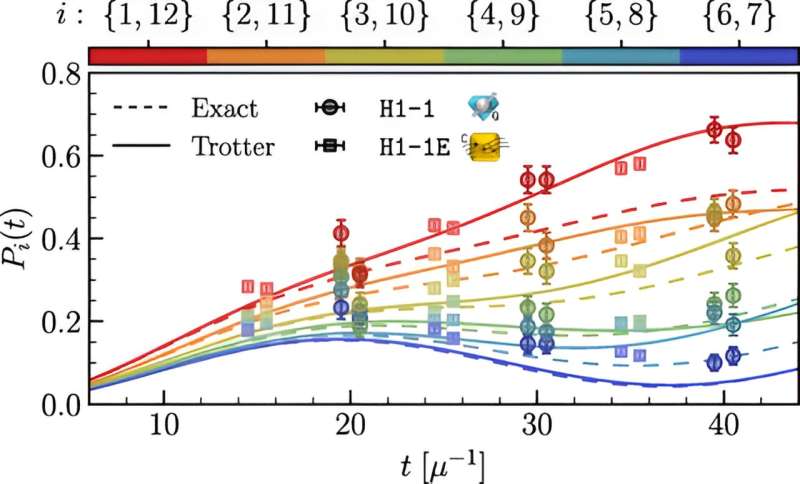
The outcomes provided a sensible approximation of how neutrinos change into entangled on the quantum degree, in order that altering the properties of 1 additionally adjustments the properties of one other. Throughout a supernova, neutrinos can change taste from an electron taste to a muon taste or to a tau taste because the neutrinos start to work together with one another and their environment. The element offered by the simulations enabled the workforce to measure the evolution from one taste to a different over time of assorted entangled neutrinos.
Why monitor the flavour conversion? As a result of the mu and tau flavors of neutrinos work together in another way with matter than their electron-flavored brethren. These interactions can affect the quantities and forms of heavier components produced within the supernova explosion.
“These circuits turned out to approximate the neutrinos’ conduct very nicely,” Savage stated. “We found we may use these simulations to measure neutrino entanglement in a statistically vital manner and that we may determine a big scaling in measurement because the variety of neutrinos elevated. This was the primary time this type of examine had been executed.”
The first hurdle for helpful quantum simulations has been the comparatively excessive error price attributable to noise that degrades qubit high quality. The issue’s so frequent the present technology of quantum computer systems has change into often called noisy intermediate-scale quantum, or NISQ.
Numerous programming strategies may also help scale back these errors, however Savage and Illa did not want these strategies to conduct their examine because of the prime quality of the Quantinuum pc’s qubits and gates. The pc’s 12-qubit circuits proved to be adequate for nearly 200 of the 2-qubit gates.
“We discovered the systematic errors on the quantum {hardware} had been lower than the statistical errors,” Savage stated. “We nonetheless have a protracted option to go to foretell the conduct of enormous neutrino programs with precision, and we do not know whether or not the present technology of NISQ units can take us there. However this system needs to be transportable to different forms of quantum computer systems, and the outcomes assist us set protocols that can be utilized to simulate bigger programs of neutrinos.”
Subsequent steps embody simulating a system of as many as 50 neutrinos. Savage hopes to mannequin such programs in quite a lot of environments.
“We need to perceive the implications of various thermal states, of states out and in of equilibrium,” he stated. “We’re excited to see what we are able to discover.”
Extra info:
Marc Illa et al, Multi-Neutrino Entanglement and Correlations in Dense Neutrino Programs, Bodily Overview Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.221003
Offered by
Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory
Quotation:
Untangling the entangled: Quantum examine shines recent gentle on how neutrinos gasoline supernovae (2024, June 22)
retrieved 22 June 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-06-untangling-entangled-quantum-fresh-neutrinos.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.