Accounts payable is an important facet of economic administration that each enterprise proprietor and finance skilled should perceive. Put merely, accounts payable refers back to the cash an organization owes its suppliers for items or providers bought on credit score.
Successfully managing accounts payable is important for sustaining wholesome money stream, fostering robust vendor relationships, and guaranteeing the general monetary well-being of your group.
A McKinsey report illustrates this level with a compelling instance. In a single firm, an audit of its accounts payable revealed lacking objects and duplications—a lot in order that the procurement managers had underestimated the corporate’s whole spend with some suppliers by as much as 90%. Take into consideration the reductions and financial savings alternatives they have been lacking out on!
Over the course of this text, we’ll aid you perceive every thing you might want to learn about accounts payable, exploring its definition, the AP course of, finest practices, and easy methods to automate the AP cycle.
What’s accounts payable?
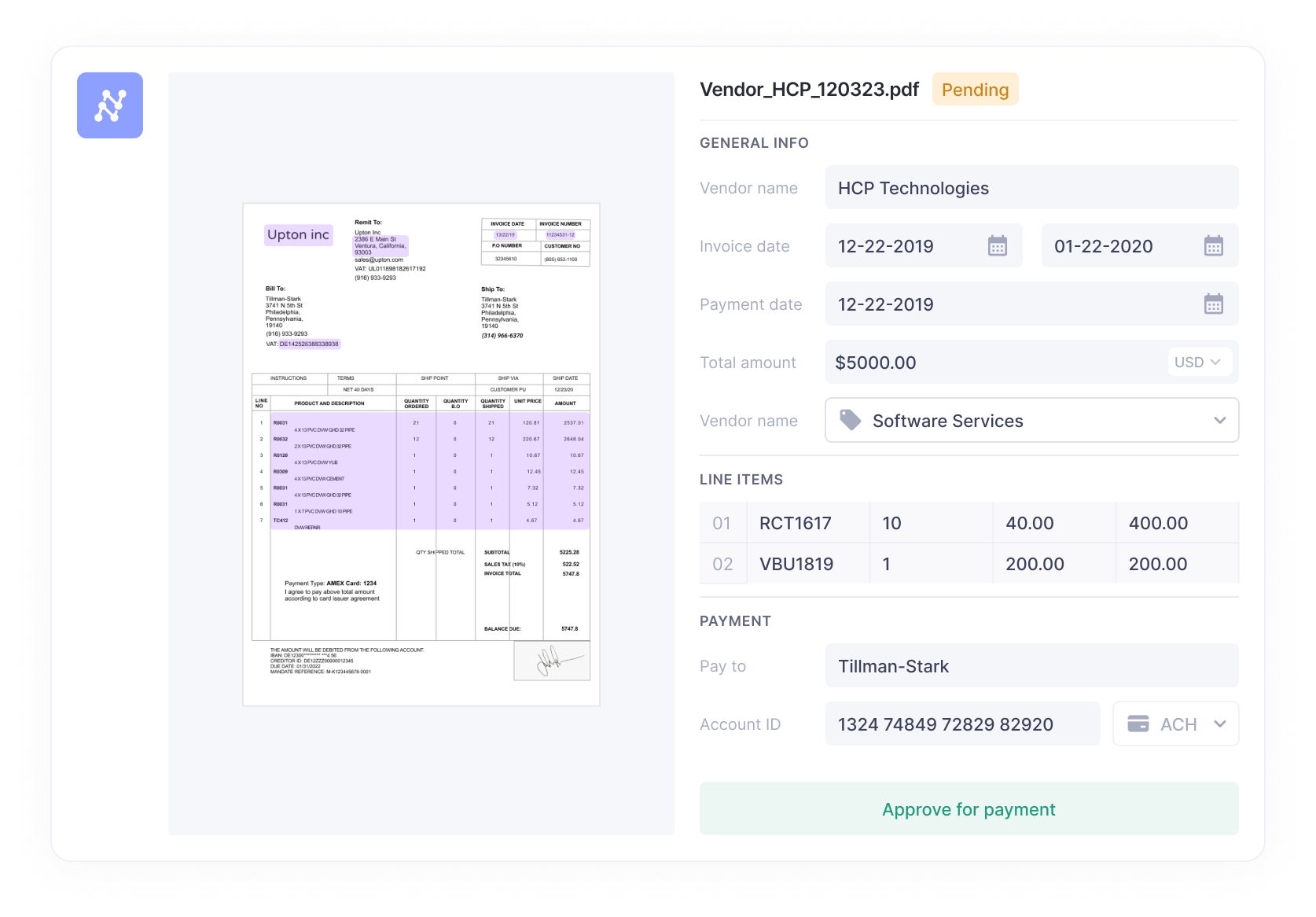
Accounts payable (AP) is a time period utilized in accounting to explain the cash an organization owes to its suppliers or distributors for items or providers bought on credit score. When an organization buys services or products from a vendor with an settlement to pay later, the quantity owed is recorded underneath the accounts payable account, a present legal responsibility on the corporate’s steadiness sheet.
The accounts payable course of includes receiving invoices, verifying their accuracy, recording them within the accounting system, and finally paying the quantity due. In a nutshell, accounts payable represents the cash an organization should pay out to its suppliers within the close to future, usually inside 30 to 90 days.
The account payable is recorded when an bill is authorized for fee. It is recorded within the Basic Ledger (or AP sub-ledger) as an excellent fee or legal responsibility till the quantity is paid. The sum of all excellent funds is recorded because the steadiness of accounts payable on the corporate’s steadiness sheet. The rise or lower in whole AP from the earlier interval can be recorded within the money stream assertion.
Efficient accounts payable administration is essential for sustaining a wholesome money stream and avoiding late fee penalties.
Examples of accounts payable bills
Listed here are just a few examples of accounts payable bills:
- Stock and uncooked supplies: Consider all of the objects you might want to create your merchandise, like metal, cloth, and plastics.
- Workplace provides and gear: From pens and paper to computer systems and printers.
- Utilities: Electrical energy, gasoline, water, and different payments that you might want to pay to maintain the enterprise operational.
- Skilled providers: Consists of charges paid for authorized recommendation, consulting, or accounting assist.
- Hire and lease funds: In case you do not personal your workplace or retail area, hire is a big account payable expense.
- Journey bills: Airfare, resorts, and meals whenever you or your staff journey for work.
- Repairs and upkeep: From fixing a broken laptop computer to sustaining your workplace’s HVAC system.
- Subscription providers: From MS Workplace 365 subscriptions to server internet hosting expenses, all of the month-to-month or yearly recurring funds for digital providers.
- Freight and transport prices: Postage, courier providers, or freight expenses billed by the transport supplier.
Save 70% on invoicing prices!
“Tapi has been capable of save 70% on invoicing prices, enhance buyer expertise by decreasing turnaround time from over 6 hours to only seconds, and unlock workers members from tedious work.” – Luke Faulkner, Product Supervisor at Tapi.
Schedule a personalised demo with us to learn the way our AP automation answer can rework your accounts payable course of and drive vital price financial savings for your online business.
The accounts payable course of
The AP cycle covers the whole lifecycle of an organization’s fee obligations, from the preliminary buy to the ultimate fee and reconciliation. The cycle begins when a division inside the firm initiates a buy request. As soon as authorized, a buy order (PO) is issued to the seller.
Upon supply, the receiving workforce checks the objects in opposition to the PO. The seller then sends an bill. That is the place the accounts payable course of actually begins.
Let’s break down the steps concerned:
Bill receipt and verification: The seller might ship the bill to the AP division through e mail, bodily mail, or an digital invoicing system. The AP workforce then verifies it for accuracy, checking particulars like the seller identify, bill quantity, date, and quantity. This step is important to stop errors or fraud.
Bill knowledge entry and GL coding: After verification, the bill particulars are entered into your accounting system and assigned applicable Basic Ledger Codes (GL Codes). These distinctive alphanumeric codes assist categorize transactions to the right normal ledger accounts, equivalent to workplace provides, utilities, or uncooked supplies.
Three-way matching and approval: The AP workforce performs a three-way match, evaluating the bill in opposition to the PO and items receipt word. That is to make sure you’re paying for precisely what you ordered and acquired. As soon as matched, the bill goes by means of your organization’s approval workflow, which can contain a number of ranges of approval relying in your insurance policies.
Cost processing and execution: After approval, the bill is scheduled for fee in response to the phrases. This includes issuing a test, initiating an ACH switch, or utilizing an organization bank card. It is necessary to maintain observe of fee dates to keep away from late charges and keep good vendor relationships.
File conserving: Lastly, the transaction is recorded in your monetary system. The AP workforce reconciles this transaction of their month-to-month shut course of and contains it of their report on excellent payables. The bill is then archived for future reference or audits. This systematic strategy ensures correct record-keeping and helps keep a transparent audit path.
All through the AP cycle, corporations may make use of numerous inner controls and approval workflows to make sure the integrity and effectivity of the method. These controls might embody segregation of duties, bill matching, and common audits to detect and stop errors or fraud.
How AP automation works

Automated bill processing saves corporations 77%, decreasing prices from $6.30 to $1.45 per bill. Automated AP software program streamlines the whole accounts payable course of by leveraging superior applied sciences equivalent to synthetic intelligence, optical character recognition, and machine studying.
Let’s check out the method:
- Seize invoices: AP automation techniques can mechanically seize invoices from numerous sources, equivalent to e mail inboxes, cloud storage, or direct integrations with vendor portals. This eliminates the necessity for guide knowledge entry and reduces the danger of errors.
- Extract knowledge: As soon as the invoices are captured, the system makes use of highly effective OCR and AI to extract related knowledge from the invoices. This contains vendor particulars, bill numbers, due dates, line objects, and whole quantities. The extracted knowledge is then validated in opposition to predefined guidelines to make sure accuracy.
- Automate workflows: Arrange customized workflows based mostly in your group’s particular necessities. For instance, you may outline approval hierarchies, arrange automated routing for various bill sorts and reminders to approvers, and configure guidelines for exception dealing with. This ensures that invoices are processed effectively and constantly, decreasing processing instances and enhancing general productiveness.
- Combine knowledge: Mechanically export and sync to your present ERP, accounting software program, and different enterprise techniques. This permits for easy knowledge stream and eliminates the necessity for guide knowledge entry throughout a number of techniques. With real-time sync, you may make sure that your monetary knowledge is at all times up-to-date and correct.
- Course of funds: As soon as invoices are authorized, you may schedule funds in response to due dates and money stream wants. Then, generate fee information, combine them together with your financial institution or fee gateway, and automate the reconciliation. This ensures well timed funds to distributors and maintains robust provider relationships.
Firms with totally automated AP processes deal with greater than double the workload. They course of 18,649 invoices per full-time worker yearly, in comparison with simply 8,689 for these counting on guide strategies.
Automate invoice pay with Nanonets
By no means chase an bill once more!
Arrange touchless AP workflows with Nanonets. Automate knowledge seize, construct customized workflows, and streamline the accounts payable course of in seconds—no code is required. See how one can slash AP prices and get rid of guide errors. E-book a personalised demo at the moment.
Right here’s a fast comparability between automated AP and guide AP workflows:
| Course of | Automated AP | Guide AP |
|---|---|---|
| Bill Processing | Quick, correct knowledge seize utilizing OCR | Gradual, error-prone guide knowledge entry |
| Matching | Automated three-way matching | Time-consuming guide comparability |
| Approval Routing | Clever, rule-based routing | Guide e mail or paper-based routing |
| Cost Scheduling | Automated based mostly on phrases | Guide monitoring and scheduling |
| Reporting | Actual-time, detailed analytics | Restricted, time-consuming guide studies |
| Error Fee | Low, with built-in validation | Larger danger of human error |
| Processing Time | Minutes to hours | Days to weeks |
| Price per Bill | Decrease, usually $1-$5 | Larger, typically $10-$30 |
What’s the position of AP in accounting?
AP is recorded as a present legal responsibility on the steadiness sheet. When an organization receives items or providers on credit score, it creates an AP entry by debiting the related expense or asset account and crediting Accounts Payable.
When the bill is paid, this entry is reversed: Accounts Payable is debited, and Money or Financial institution Account is credited. This double-entry system ensures that the corporate’s books stay balanced and precisely mirror its monetary place.
AP vs. AR
Whereas Accounts Payable represents cash owed by an organization, Accounts Receivable (AR) represents cash owed to an organization by its clients. The important thing variations are:
- Stability sheet place: AP is a legal responsibility; AR is an asset.
- Money stream affect: AP decreases money when paid; AR will increase money when collected.
- Monetary objectives: Firms purpose to increase AP phrases whereas decreasing AR assortment instances.
AP vs. Commerce Payable
Whereas typically used interchangeably, AP and Commerce Payables have delicate variations:
- Scope: AP contains all short-term money owed owed to collectors, whereas Commerce Payables particularly confer with quantities owed to suppliers for items or providers straight associated to the corporate’s core enterprise.
- Monetary reporting: Some corporations might separate Commerce Payables from different payables on their steadiness sheet for extra detailed reporting.
- Utilization: Commerce Payables are sometimes utilized in monetary ratios particular to provider relationships and stock administration.
What does the AP division do?
The accounts payable division manages an organization’s monetary obligations to suppliers and repair suppliers. Its core features embody bill administration, fee processing, provider relations, monetary record-keeping, and coverage compliance.
These obligations are usually distributed amongst numerous roles equivalent to AP clerks, fee processing analysts, exceptions analysts, vendor administration specialists, and AP managers.
AP professionals in small companies typically deal with a number of roles and juggle many obligations concurrently.
Listed here are among the widespread obligations dealt with by accounts payable:
- Amassing, sustaining, verifying, recording and sharing enterprise transactions.
- Flagging invoices or transactions.
- Getting requisite approvals or signatures for explicit transactions
- Making a paper path for every fee and reconciling financial institution statements.
- Veryfing invoices and funds by matching them or reconciling them with supporting paperwork.
- Evaluate line objects and totals on invoices to stop fraud, errors & double funds.
- Preserving observe of grasp vendor knowledge, assigning voucher numbers, and sustaining vendor correspondences.
- Talk accounting and spend insurance policies with the corporate and huge.
- Put together a system of checks and balances.
Organizations, on uncommon events, additionally outsource AP features to exterior businesses.
How one can monitor your AP effectivity?
At all times measure your organization’s AP course of effectivity to determine areas for enchancment. This may allow you to proactively determine cashflow points and optimize working capital.
Regulate these AP indicators to observe and enhance your AP course of:
- Days Payable Excellent (DPO): Measures the common variety of days an organization takes to pay its suppliers. A better DPO can point out higher money administration however might pressure provider relationships if too excessive. Method: DPO = (Common Accounts Payable / Price of Items Bought) x 365
- Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio: Signifies what number of instances an organization pays off its common accounts payable throughout a yr. A better ratio suggests the corporate is paying suppliers extra shortly. Method: AP Turnover Ratio = Price of Items Bought / Common Accounts Payable
- Share of Early Funds: Exhibits the proportion of funds made earlier than the due date. This could point out potential for capturing early fee reductions however may counsel inefficient money administration. Method: (Variety of Early Funds / Whole Variety of Funds) x 100
- Share of Late Funds: Displays the proportion of funds made after the due date. Excessive percentages might point out money stream points or inefficient processes. Method: (Variety of Late Funds / Whole Variety of Funds) x 100
- Bill Processing Time: Measures the effectivity of the AP course of from receipt to fee of an bill. Shorter instances usually point out extra environment friendly processes. Method: Common time from bill receipt to fee
- Bill Exception Fee: Exhibits the share of invoices that require guide intervention. A excessive price might point out points with provider invoicing or inner processes. Method: (Variety of Invoices Requiring Guide Intervention / Whole Variety of Invoices) x 100
- Price Per Bill: Measures the whole price of processing an bill. Purpose to maintain it lower than $3 per bill. Method: Whole AP Division Prices / Whole Variety of Invoices Processed
- Money Conversion Cycle (CCC): Measures how shortly an organization converts investments into money flows from gross sales. A decrease CCC is healthier. Method: DSO + DIO – DPO
- Working Capital as a Share of Income: Signifies how effectively an organization is utilizing its working capital to generate income. A decrease proportion usually signifies extra environment friendly use of working capital. Method: (Present Belongings – Present Liabilities) / Income x 100
Common monitoring and evaluation of those KPIs can present invaluable insights into the AP division’s functioning, pinpoint areas of concern, and spotlight alternatives for enchancment. These metrics permit companies to streamline their AP processes, cut back errors, and enhance vendor relationships.
Closing ideas
Accounts payable is an important perform for any enterprise. However why cease at guide processes when automation can revolutionize your AP division? By implementing AP automation, you may considerably cut back processing prices, decrease errors, and unlock invaluable time for strategic duties.
Nanonets can streamline your complete AP course of, from bill seize to fee execution. This not solely improves effectivity but additionally enhances vendor relationships and gives higher visibility into your monetary knowledge. As companies develop, the necessity for environment friendly AP automation turns into more and more essential.
Schedule a demo with us to see how Nanonets can rework your accounts payable course of.
FAQs
What’s the position of accounts payable?
Accounts payable manages an organization’s excellent money owed to suppliers. Key obligations embody processing invoices, guaranteeing correct and well timed funds, sustaining vendor relationships, stopping fraud, and optimizing money stream. AP groups additionally deal with expense reporting and compliance.
What’s the distinction between accounts payable & accounts receivable?
Accounts payable is the cash that your online business owes to suppliers or distributors. Accounts receivable is the cash that your clients owe to your online business. The previous represents outflows of money whereas the latter describes inflows. Additionally, discover distinction between accounts payable and notes payable.
What are the 4 features of accounts payable?
The 4 essential features of the accounts payable division are:
- Obtain, course of, and confirm invoices
- Authorize and schedule funds to distributors
- Keep correct information of transactions
- Handle vendor relationships (negotiate fee phrases, resolve disputes, guarantee well timed funds)
Which sort of account is accounts payable?
Accounts payable is taken into account a present legal responsibility account. This implies it is an obligation the corporate should repay inside the subsequent yr. Identical to different legal responsibility accounts, accounts payable will increase with a credit score entry. When the corporate pays off the payables, it debits accounts payable. One of these account is essential in managing money stream and sustaining good relationships with suppliers.
How one can calculate accounts payable?
If a enterprise begins the yr with $5,000 in accounts payable, makes $20,000 in credit score purchases all year long, and makes funds of $15,000 to suppliers, the ending accounts payable could be:
Ending Accounts Payable = ($5,000 + $20,000) – $15,000
Because of this the enterprise has $10,000 in excellent payables on the finish of the yr. Preserving observe of this quantity helps companies handle their money stream and guarantee they’re assembly their obligations to suppliers.
The complete-cycle AP covers the entire accounts payable course of, beginning with buy requisition and bill technology and ending with remaining fee and reconciliation. This includes creating buy orders, receiving items, processing invoices, approving funds, executing transactions, and managing vendor relationships.
What are the steps within the accounts payable course of?
- Bill receipt
- Knowledge entry and coding
- Verification and matching
- Approval routing
- Cost processing
- Cost execution
- Reconciliation and record-keeping
How is account payable handled in accounting?
Accounts payables are handled as a present legal responsibility on the steadiness sheet. They characterize cash owed to suppliers for items or providers acquired however not but paid for. AP will increase when invoices are acquired and reduces when funds are made.
How do you document accounts payable in accounting?
To document accounts payable:
- Credit score the AP account when an bill is acquired
- Debit the corresponding expense or asset account
- When paying, debit AP and credit score money
How do you document accounts payable in accounting?
When recording an bill: Debit: Expense/Asset Account Credit score: Accounts Payable
When paying an bill: Debit: Accounts Payable Credit score: Money/Financial institution Account






























![[2409.12947] Unrolled denoising networks provably study optimum Bayesian inference](https://i0.wp.com/arxiv.org/static/browse/0.3.4/images/arxiv-logo-fb.png?w=218&resize=218,150&ssl=1)















